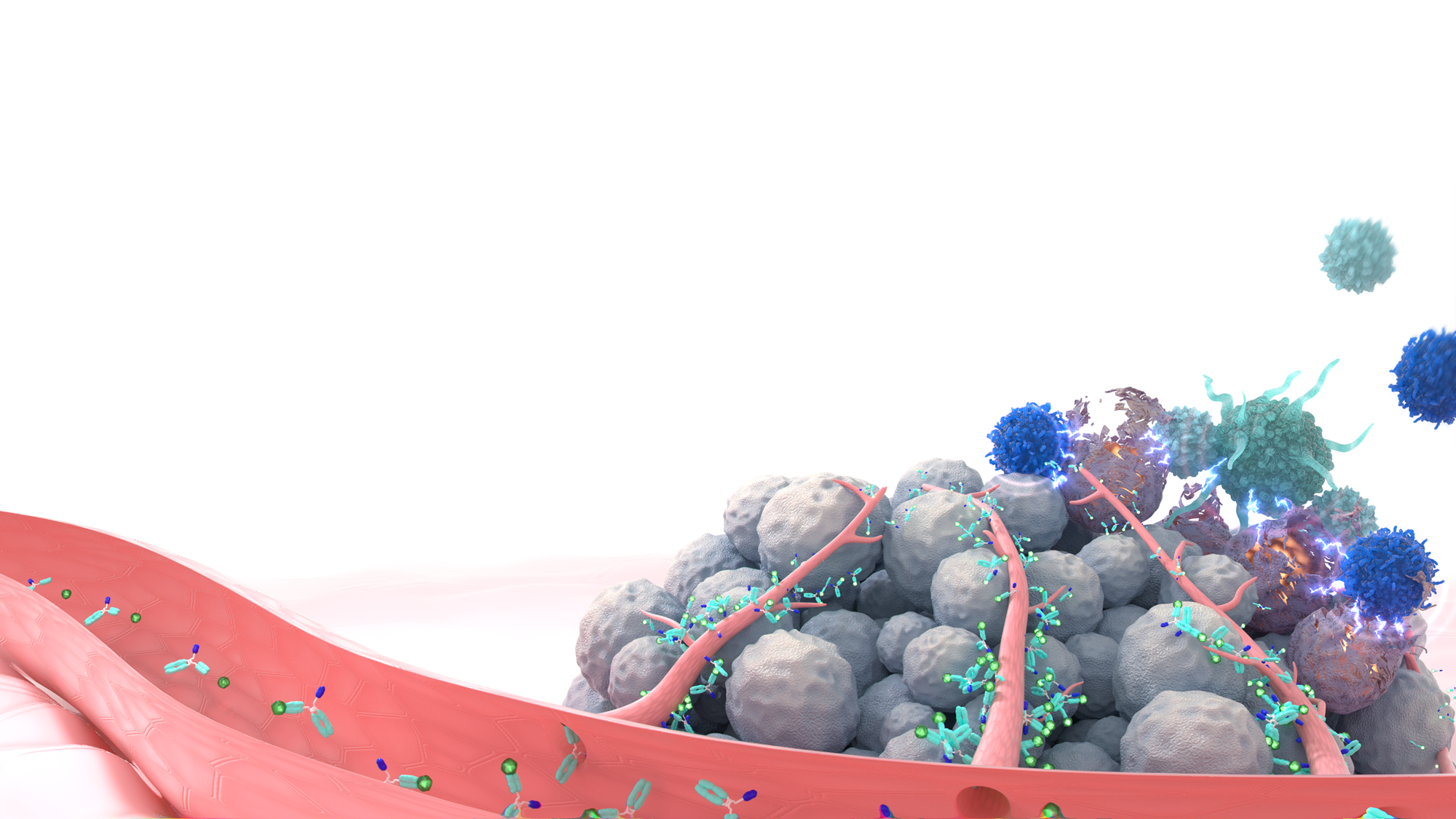
Reshaping the future for patients with non-immunogenic tumors
By pioneering targeted immune stimulation, our unique mode of action, we develop a groundbreaking class of cancer therapies that will form the future treatment paradigm for non-immunogenic tumors.
Science
IFNγ is a potent driver of immune infiltration in cold tumors
Cold tumors need new therapies
Immunotherapies such as checkpoint inhibitors are highly efficient in many solid tumor types. However, immune cells need to be present in the tumor micro-environment (TME) for these immunotherapies to work. Cold tumors, or non-immunogenic tumors, secrete suppressive molecules and mutate their cellular markers which prevents immune cells from entering the TME, rendering immunotherapies ineffective.
IFNγ injections are potent but dangerous
Interferon gamma (IFNγ) is a powerful anti-tumor cytokine that has been linked in the clinic to induce immune cell infiltration and activation in the TME. However, previous attempts to use recombinant IFNγ therapeutically have resulted in side-effects due to rapid spikes in systemic cytokine levels and limited efficacy due to low accumulation in the TME.
TIMS enables IFNγ potency in a safe way
Cymab’s novel Targeted Immune Stimulation (TIMS) technology solves this by binding free, endogenous IFNγ with our novel antibody which prolongs IFNγ half-life and hence its exposure to the tumor. IFNγ levels in the tumor are thereby increased without side-effects associated with rapid raising of systemic IFNγ concentrations. Tumor accumulation and efficacy can be further increased via addition of an antigen-targeting domain to our antibody, when needed. TIMS transforms cold tumors into immune-active sites, enabling tumor cell killing as a monotherapy and significantly enhancing immunotherapy efficacy in combination therapy.
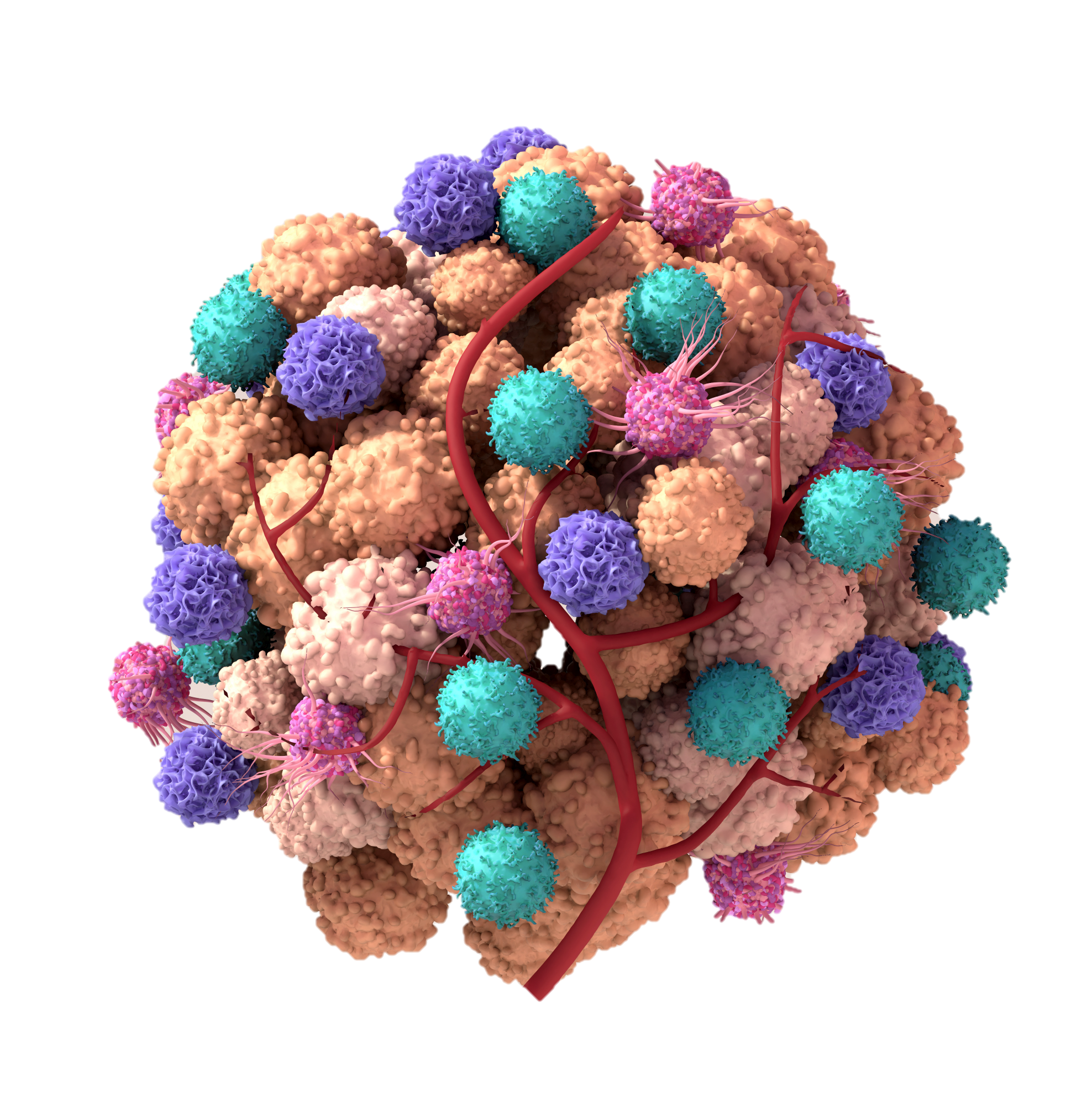
Technology
Our Targeted Immune Stimulation (TIMS) technology accumulates endogenous IFNγ in a novel way
1.
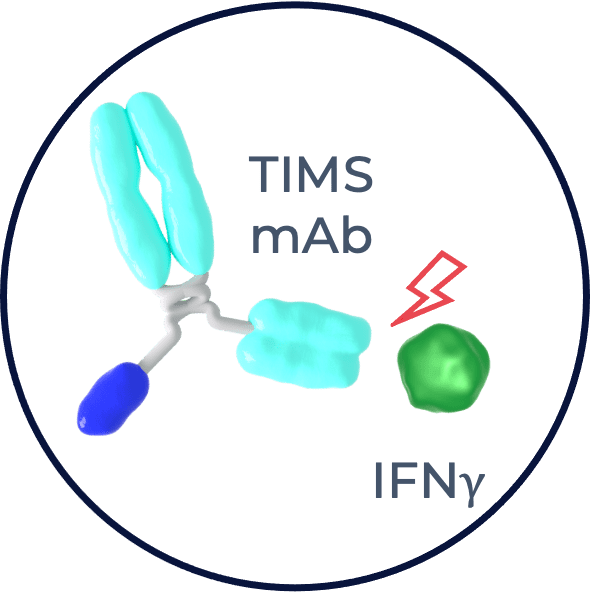
Binding the body’s own IFNγ
Read more
When injected into the blood stream, our TIMS antibody binds to circulating IFNγ with one of its binder arms. Binding to IFNγ is optimised to promote IFNγ’s anti-cancer activity at the tumor site.
2.
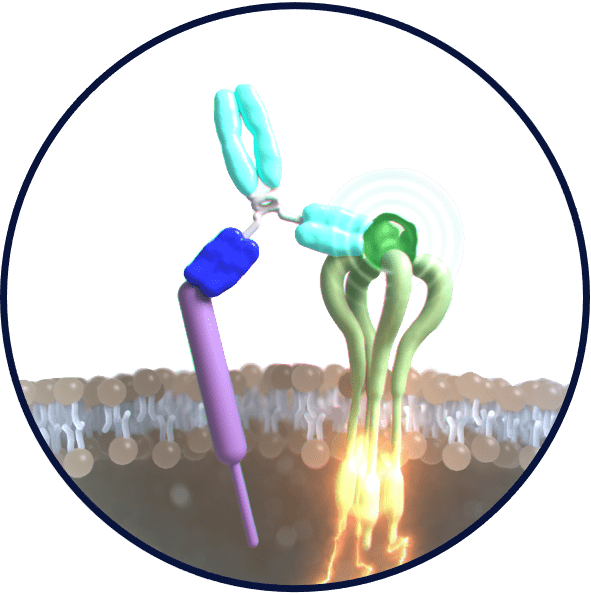
Accumulating IFNγ into tumors
Read more
Bound IFNγ accumulates at the tumor site due to the enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR) inherent to antibodies in tumor tissues. Once accumulated in the tumor, the bound IFNγ engages with its receptor on tumor cells to initiate chemokine (CXCL10) secretion and MHC-I expression, which attracts immune cells to the tumor, as well as PD-L1. Addition of a second antigen binder arm has the potential to further enhance tumor accumulation and efficacy when needed.
3.
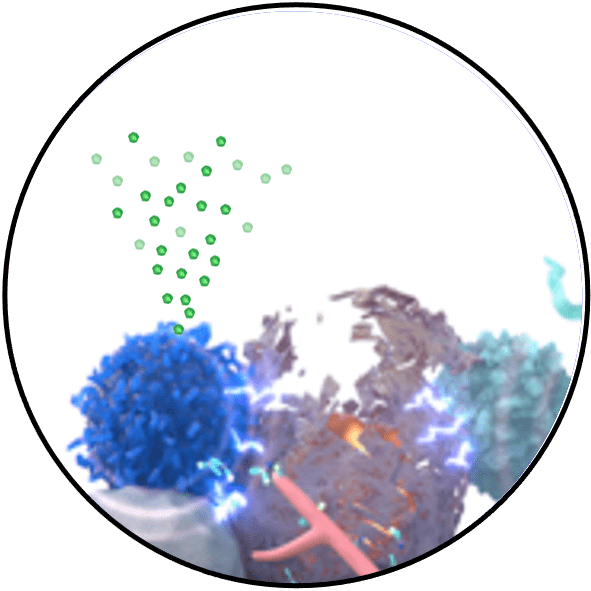
Killing tumor cells
Read more
Infiltration of immune cells alters the tumor microenvironment and induces potent tumor killing. In response to tumor cell recognition, the infiltrated immune cells also secrete IFNγ which is captured and sustained by free TIMS antibodies, kick-starting a positive feedback loop of anti-cancer activity. In addition to the anti-tumor effect, immune cell infiltration also enables previously ineffective immunotherapies to work again.

Pipeline
IFNγ modulation &
accumulation
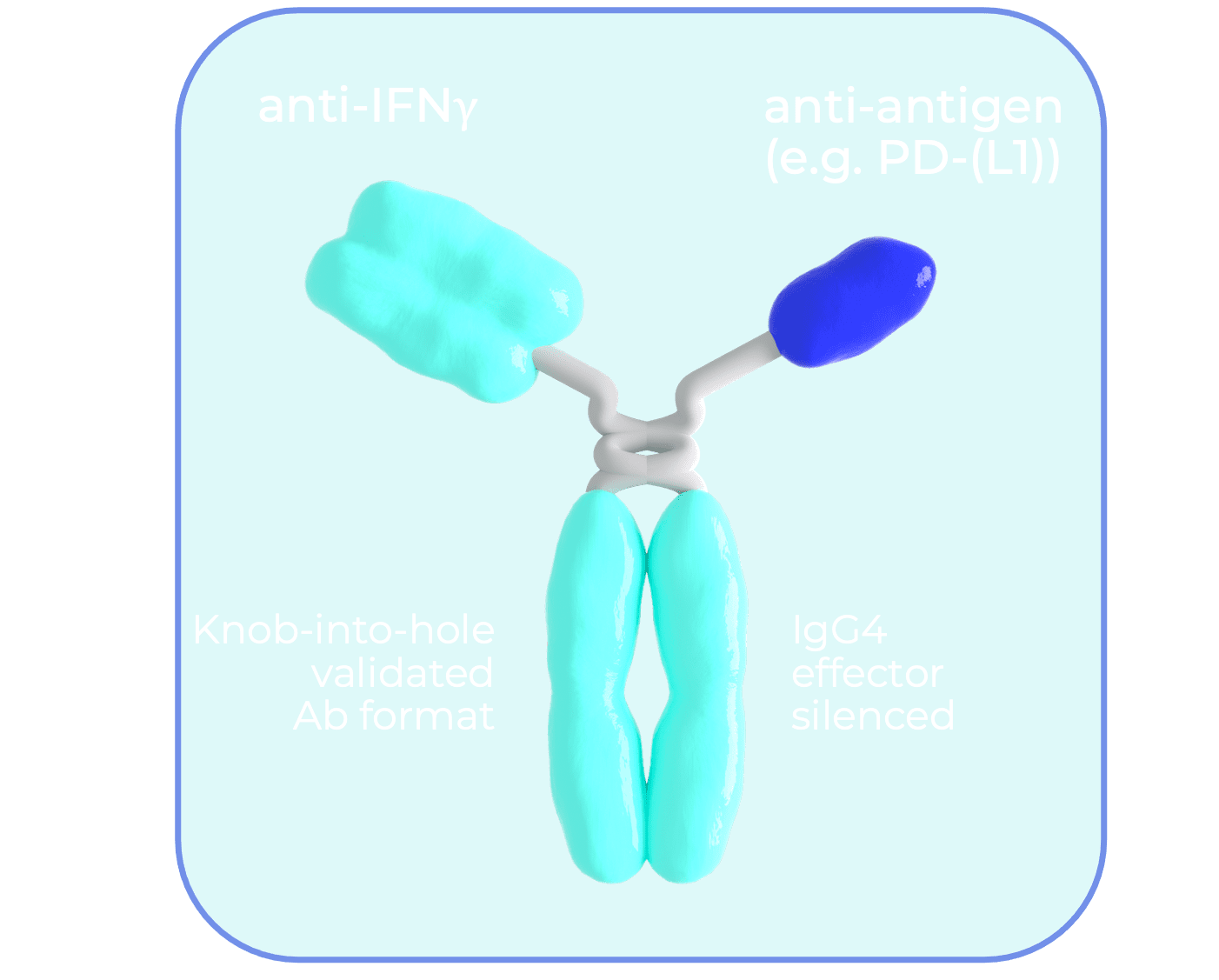
Our TIMS bispecific antibodies capture endogenous IFNγ for improved systemic safety profile
Antibody binding prolongs IFNγ half-life and hence its exposure to tumor cells
IFNγ is accumulated in tumor tissue via inherent antibody characteristics (i.e.: EPR effect) that leverage the increased vasculature and hence blood flow to tumors.
The TIMS technology uses validated bispecific antibody formats with a clear and de-risked CMC path
Antigen targeting &
blocking
In addition to IFNγ, our antibody binds to a “pro-cancer” antigen on either tumor or immune cells.
Whilst not required for initial accumulation, this antigen binding further prolongs IFNγ exposure within the tumor. Moreover, it enables an additional mode of action via inhibition of pro-cancer antigens such as PD-1 or PD-L1.
The platform potential of our bispecific antibody is enabled by the modularity of the second binding arm target.
Team
Experienced Leadership Team, Leading Advisors
Core team
Board of directors
Scientific advisors
News
Latest news from around the world
Supported by




Careers
Join Cymab in reshaping the future of cancer treatment
There are currently no available positions, but please reach out for unsolicited applications.